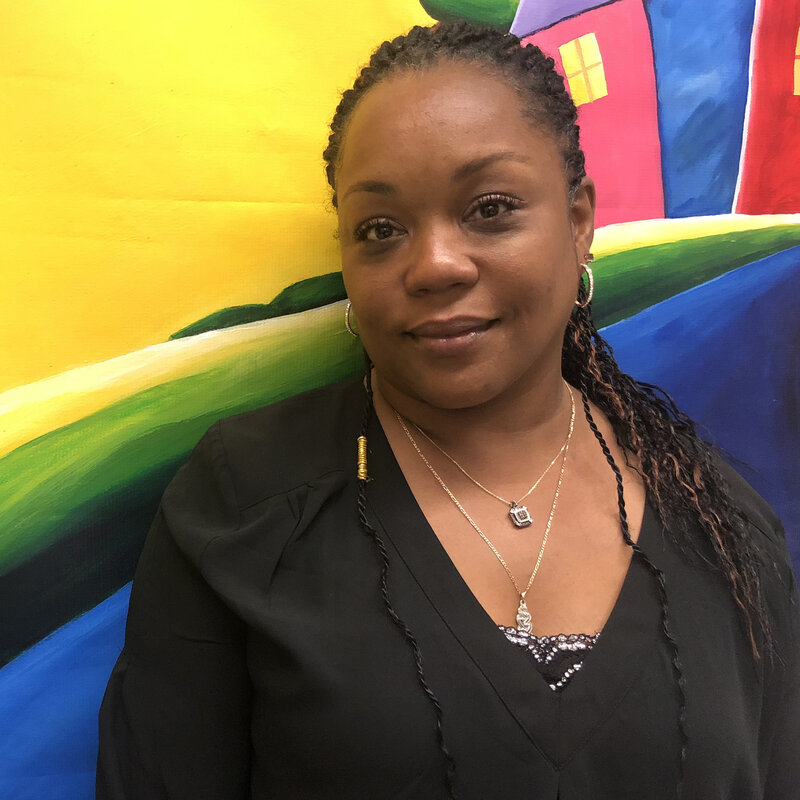
Latosha Poston says she made a lot of mistakes in her life. Her legal troubles began in her teens after her first child was born in Indianapolis. Over the years, bad decisions led to some arrests, some convictions.
Latosha Poston says she made a lot of mistakes in her life. Her legal troubles began in her teens after her first child was born in Indianapolis. Over the years, bad decisions led to some arrests, some convictions.Barbara Brosher/Indiana Public Media
Latosha Poston says she made a lot of mistakes in her life. Her legal troubles began in her teens after her first child was born in Indianapolis. Over the years, bad decisions led to some arrests, some convictions.
"Sometimes we get stuck in our past and let our past guide us," she says.
The 44-year-old has worked hard to straighten out her life. But her criminal records — all involving misdemeanors — continued to haunt her as she tried to find a decent job and place to live.
Then, while watching the local news, she heard about Indiana's Second Chance law, passed in 2013. It allows people to petition to remove their misdemeanor convictions and arrests from public view.
Indiana is among several states to change their approach to the restoration of a person's rights and status after an arrest or conviction. In the last two years, more than 20 states have expanded or added laws to help people move on from their criminal records — most involve misdemeanors. Marijuana legalization and decriminalization have played a big role in driving these reforms. Fairness is another factor, with lawmakers from both parties rethinking the long-term consequences of certain criminal records, as well as the economic impact of mass incarceration.
There are also purely economic reasons to encourage the sealing of criminal records.
"It hurts communities, it hurts counties and it hurts states if their citizens cannot be productively employed or aren't part of the tax base," says American University law professor Jenny Roberts, who has written extensively on the collateral consequences of convictions. "So there's certainly an economic incentive for allowing people to move beyond their criminal record."
The state-level reforms have helped tens of thousands of people across the United States.
Poston of Indianapolis is among them. After working in home health care for nearly 20 years and making just over $11 an hour, she landed a much better-paying job in a hospital as an operating room assistant once her records were sealed.
"I felt like something was lifted off," she says of her case. "Because now I kind of felt like a human."
With background checks ubiquitous for jobs, schools, mortgage applications and more, even one conviction — and sometimes even just one arrest — can dog people for years, critics say, relegating them to permanent second-class status.
"No one should underestimate how much even the most minor of misdemeanor convictions — including marijuana or trespassing or any kind of conviction — can affect someone's ability to get a job, to get housing and to function fully in society," says Roberts, who also co-directs the Criminal Justice Clinic at American University in Washington, D.C.
Time for change
The reform trend reflects an emerging consensus that the social and economic problems created by mass prosecution and incarceration call for a fundamental reimagining of the criminal justice system.
While reformers largely welcome the moves by states, there's concern that a patchwork of laws as well as steep legal fees, prosecutorial foot-dragging and other barriers have blunted what is otherwise seen as a rare area of bipartisan, effective reform.
 |
Barbara Brosher/Indiana Public Media
|
She and others are calling on the National Conference of State Legislatures, the National Center for State Courts and the American Bar Association to study and share what reforms are showing the most promising outcomes.
"Right now it's getting harder for state legislatures to pick out a single approach," Love says. "We have to start looking at this in a more systematic way and look at what works best."
For example, there's a growing body of evidence that it undermines public safety if you don't help people move beyond their criminal records and participate in the workforce. Without that help, the chance of people returning to the criminal justice system increases.
One study estimates that the unemployment rate for formerly incarcerated people is more than 27 percent — far higher than the total U.S. unemployment rate during any historical period, including the Great Depression. The rate is even higher for African-Americans who've had run-ins with the law.
With the national jobless rate at historical lows, many companies are looking at new ways to hire additional workers. A recent survey showed that more than 80 percent of managers — and two-thirds of human resource professionals — "feel that the value workers with criminal records bring to the organization is as high as or higher than that of workers without records."
Indiana's example
As in many other states, the work of sealing and expungement in Indiana mostly falls to nonprofit legal groups and private attorneys. But in Marion County, the prosecutor's office has hired a full-time paralegal to process all requests. The county has had more than 11,500 people come through since legislators implemented the law.
While the mood nationally surrounding expungement has dramatically improved, some prosecutors and judges remain skeptical or outright opposed to records clearing. Philosophically they don't think those who've broken the law should get a clean slate.
So it helps a lot that in Marion County, which encompasses Indianapolis, Prosecutor Terry Curry fully supports the effort. He advocated for the law because he thinks people who've stayed out of trouble shouldn't carry the legal stain forever.
"If our goal is to have individuals not reoffend, then in our mind it's appropriate to remove obstacles that are going to inhibit their ability to become productive members of our community," Curry says.
While most cases in Indiana involve misdemeanors, judges have discretion with violent-felony petitions. Victims of those crimes also can give testimony. More serious felonies can be expunged eight or 10 years after the completion of the sentence.
Some crimes must have the prosecutor's written consent for expungement. Homicides and some sexual offenses are not eligible for expungement in Indiana and in most other states.
You can petition to have records for convictions expunged only once in your lifetime. If you are convicted of other charges later on, there's no chance of having them sealed.
While the process in Indiana and in other states seems simple, serious hurdles remain. Expungement can be time consuming and costly. There are filing fees for every petition — fees not everyone can afford.
In addition, the process can vary from county to county depending on cooperation from local prosecutors. Advocates in Indiana want lawmakers to make it easier for people to expunge their records — regardless of where they are in the state.
Getting the word out
Even more vexing — in Indiana and throughout the country — is the general ignorance about existing expungement laws. People just don't know they exist or how they work.
Public defenders from New York to Los Angeles say they have to do a better job of both getting the word out and pushing states to better fund these efforts.
At a recent LA-area expungement clinic, a man showed up who'd done significant prison time for a nonviolent felony. And he'd been off probation for more than five years. He still couldn't get a job. The man, who didn't want his name used, thought at first the expungement clinic was some kind of scam.
"He had no idea he could not only get it [the felony] expunged but reduced to a misdemeanor," says Los Angeles County Deputy Public Defender Lara Kislinger, who was helping him with the paperwork. "He just had no idea. And he was so grateful. And he's been having so much trouble finding a job. And we want people to be able to re-enter society and be productive members of society. And this was a case where it was so obvious it was holding up jobs — and life. And it's tragic."
Expanding public knowledge of sealing and expungement laws takes money and effort. Many public defender offices already are overwhelmed, understaffed and underresourced.
How long should a record last?
Across the nation, felonies are harder to expunge and involve longer waiting periods, and in many states, homicides and certain sexual offenses are almost impossible to expunge.
 |
Philip Cheung for NPR
|
California has taken the lead in reducing incarceration and prosecution of certain low-level drug crimes and nonviolent felonies following the passage of Proposition 47 and other measures. Past offenders can petition a court to reduce their crimes to misdemeanors.
Supporters say it has helped reduce the prison population and racial disparities in the justice system while saving taxpayers money. Funds are redirected, for example, into support services such as drug treatment and counseling.
Others say Proposition 47, while a good start, is inadequate. Jay Jordan of Los Angeles served seven years in prison for robbery. He has been out now for nearly eight years and says he still faces daunting obstacles to full re-entry into society.
"You know, I tried to adopt and was turned down. Tried to volunteer at school and was turned down. Tried [to] sell insurance, was turned down. Tried to sell used cars, was turned down. So, you know, every single step of the way when I try to better myself and, you know, be able to take care of myself for my family, there are these massive barriers," Jordan says. "And I'm not alone."
Indeed, there are some 8 million formerly incarcerated people in California. In the U.S., it's estimated that there are some 60 million people with a criminal record, according to federal statistics. The majority are misdemeanors. One report estimates as many people have criminal records as college diplomas.
Jordan now works for a nonprofit that advocates for rights of the formally incarcerated. In their work, Jordan and others are asking the basic question — how long should these convictions be on people's records if they've done their time and are working to become good citizens?
Not everyone wants these reforms. In California, some want to roll back parts of the state's criminal justice reforms through a proposed 2020 ballot initiative that would, among other things, reduce the number of inmates who can seek earlier parole and reclassify some theft crimes from misdemeanors to felonies.
"Proposition 47 was approved overwhelmingly by California voters who understood that permanently punishing people for a past mistake is not reflective of our shared American values nor is it an effective safety strategy," says Jordan, who directs Californians for Safety and Justice's #TimeDone/Second Chances campaign.
"Everyone who has an old, low-level, nonviolent felony on their record that is eligible for reduction to a misdemeanor under Prop. 47 should be able to get relief, and we want to make that as easy as we possibly can for folks," he says. "People deserve the chance to overcome the mistakes of their past, and that road to redemption should be as smooth as possible."
Some Democratic lawmakers in California are pushing back with proposed legislation that would automate the expungement process for all felonies that are eligible for reduction under the law.
Legal experts like Roberts, the American University law professor, caution that the best solution might be for prosecutors to simply take fewer minor cases to court in the first place.
"I don't think you can have an actual conversation about sealing and expungement and decriminalization until you talk about less prosecution and less funneling of low-level misdemeanors into the criminal justice system," Roberts says.
Explained: Misdemeanors, Felonies, Pardons, and Expungements
Companies Hire Felons | Companies That Hire Felons | Companies That Hire Ex-offenders | Employers That Hire Ex-offenders | Employers That Hire Felons | Jobs For Felons | Jobs For Ex-offenders | Jobs That Hire Felons | Resumes for Felons | Felon Friendly Jobs | Felon Friendly Employers | Jobs for Felons | Jobs For People That Have Felonies | Jobs For People With A Criminal Record | Expungement
Scrubbing The Past To Give Those With A Criminal Record A Second Chance
Eric Mayo